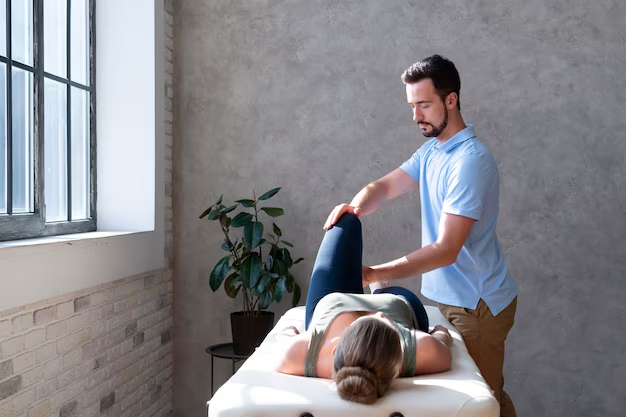

This is a method of manual therapy related to the spine, ligaments, and connective tissue with controversies that grow out from both its fans and opponents. Many patients testified to its benefits while some others rejected it because of lack of scientific proof, efficiency, and in comparison with other therapies. It will be very essential for anybody who might consider Naprapathic care to be aware of these challenges and controversies so he could make a balanced view of the benefits and limitations attached to this particular care.
What are the main criticisms of Naprapathy?
The main criticisms of Naprapathy often focus on its lack of extensive scientific research, limited recognition in mainstream medicine, and skepticism about its efficacy. Many argue that more clinical studies are needed to validate its long-term benefits. Critics also question its scope compared to other therapies.
There are also attacks towards naprapathy because of little coverage in mainstream medical literature. The effects cannot be proven profoundly, according to some, based on patient relief, whereas controlled studies are necessary to prove it definitively. The field further lags behind in recognition in various countries, thereby making it more arduous for practitioners to operate on a bigger scale. Critics of naprapathy also indicate that there is a requirement for more clinical comparison research with other therapies to establish a clearer view of its potential.
Why is Naprapathy not widely accepted in mainstream healthcare?
Naprapathy is not widely accepted in mainstream healthcare due to the lack of clinical trials, limited professional recognition, and its overlap with other manual therapies. The absence of strong scientific evidence hinders wider acceptance in medical communities globally.
Controlled clinical studies on the effectiveness of Naprapathy have therefore been relatively few in number and have slowed its acceptance in mainstream health services. Overlapping Scope: Another reason is that the scope of Naprapathy often overlaps with that of other types of manual therapy, such as chiropractic.
It is not always possible to differentiate between specific value contributions. Other regions even do not formally recognize the practitioners of Naprapathy, which still restrains its growth and limits patient accessibility. This scientific basis could be further strengthened by research studies, which may also lead to opening up more doors for greater healthcare acceptance.

How does Naprapathy differ from chiropractic care?
Naprapathy differs from chiropractic care by focusing on soft tissue manipulation and the connective tissues surrounding the spine, whereas chiropractic care primarily involves spinal adjustments. Naprapathy aims to address chronic conditions by improving ligament function and tissue flexibility.
Chiropractic care is rather different compared to Naprapathy because Naprapathic views connective tissues such as ligaments and tendons in order to handle tissue elasticity alongside spinal adjustments. This brings the treatment within Naprapathy to a far greater scope – beyond just adjusting the spine alone – to focus on problems such as chronic muscle and ligament stiffness, among others. The two may be used in tandem, but they are vastly different in terms of techniques and areas of focus.
What scientific evidence supports Naprapathy’s effectiveness?
Scientific evidence supporting Naprapathy’s effectiveness is limited but growing. Some small-scale studies have shown improvements in musculoskeletal pain relief, but large-scale clinical trials are still needed. Critics emphasize the importance of more rigorous research to validate its claims.
The science currently remains minor, although there are some studies that prove that Naprapathy helps reduce musculoskeletal pain. Small-scale trials suggest that patients feel relieved, especially concerning localized pain in the back, and issues with ligaments.
However, more clinical trials with higher and more rigorous standards are required to ensure Naprapathy is comparable to other manual therapies at best. Without such studies, then from the scientific and medical world, will be silenced.
Can Naprapathy be considered a holistic therapy?
Naprapathy can be considered a holistic therapy as it focuses on the body’s connective tissue health, aiming to treat underlying causes of pain. It also considers lifestyle and overall well-being, making it more comprehensive than some manual therapies.
It promotes the healing of not only the immediate symptoms of musculoskeletal pain but also the underlying conditions related to tissue flexibility and ligament function. Often, advice on lifestyle, posture, and exercise is incorporated into treatment so that the root cause of discomfort receives consideration, distinguishing it from more treat-the-symptom activities.
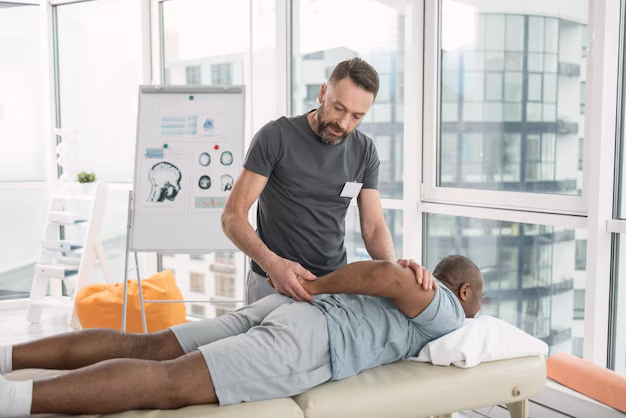
How does Naprapathy handle chronic pain?
Naprapathy handles chronic pain by targeting the connective tissues and ligaments, improving flexibility and reducing tension. Treatments often involve soft tissue manipulation and stretch to address pain’s underlying cause, offering long-term relief.
This approach of Naprapathy takes care of the body’s connective tissues, relieving chronic pain and not being just a symptom. Using manual manipulation, stretching, and rehabilitation exercises, reduces inflammation and tension in the affected areas.
Normally, patients experience gradual improvements due to their increase in flexibility and subsiding tension. The focus on long-term results makes Naprapathy different from temporary treatments.
What are the controversies surrounding Naprapathic education?
The controversies surrounding Naprapathic education stem from differing standards between countries, lack of universal accreditation, and its comparison with other medical degrees. Critics argue that the education system needs more rigorous standards and research-based curricula.
For example, the dissimilarities among various countries have often subjected Naprapathic education to criticism at times. In some regions, the path in terms of educational procedure and process for Naprapathy is not deemed as strict as that of a medical or chiropractic degree; hence, it raises a doubt regarding the curriculum’s authenticity.
A more research-oriented curriculum would be really helpful to bring Naprapathic education to the level of other health care disciplines, argument critics. These controversies are often related to how best to support and recognize the profession of Naprapathy in the clinical practice context.
In Conclusion
Naprapathy remains widely criticized and controversial, particularly in terms of its scientific basis, training, and professional recognition. Many clients, however still report clinically important benefits as a result of Naprapathic treatment. The field will have a higher likelihood of greater general acceptance as research continues. Understanding the criticisms, though, allows for a more balanced view so that patients can make informed decisions regarding Naprapathic treatment.

