Becoming a Practitioner of Osteopathy: A Step-by-Step Guide
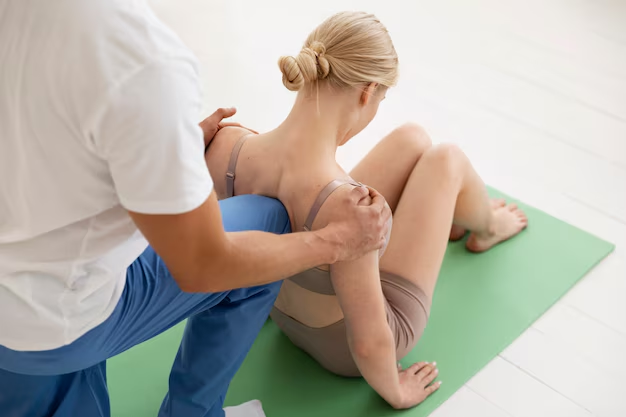

This requires an understanding of the body, osteopathic manual techniques, and an attention to the philosophy of holistic care. Whether you find yourself being led to wanting to help others become healthy, or maybe into this field of alternative medicine, you will require education and commitment in order to obtain a license as an osteopath.
What qualifications do you need to become an osteopath?
To become an osteopath, you need to complete a degree in osteopathy, typically a five-year program. This includes both theoretical knowledge and practical experience. Afterward, you must pass a licensing exam to practice.
The program entails subjects like anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and manual therapy techniques. After finishing the program, graduate osteopaths should sit a professional license exam in their country to be lawfully licensed and permitted to practice. Some countries require practitioners to register with certain professional organizations, and continued education might be necessary to maintain a license.
How long does it take to become an osteopath?
Becoming an osteopath usually takes five years, which includes both academic study and clinical training. After completing the program, additional time may be needed for licensing exams and registration.
This training will place equipping students with expertise in diagnosing and treating patients in the use of osteopathic principles. Having finished this degree, often after completing it, graduates have to take a licensing examination and register before a professional board, something which adds some time to the period in some countries.
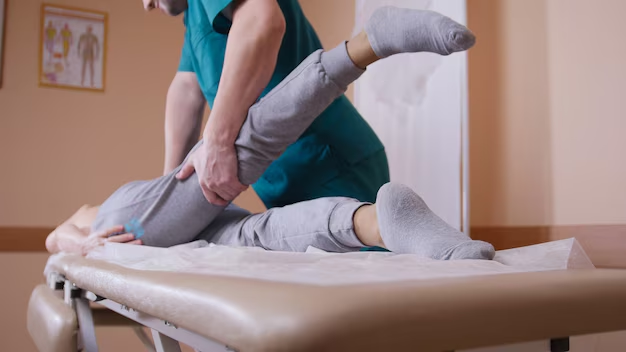
What subjects are covered in an osteopathy degree program?
An osteopathy degree program covers subjects such as anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and manual therapy techniques. Clinical training is also an essential part of the curriculum.
Students are also exposed to biomechanics-the study of the way the human body moves-and techniques in manual therapy such as joint manipulation and soft tissue massage. Osteopathic theory is subsequently combined with clinical practice, where hands-on training takes place. In this, the students can apply what they have learned into practice; the graduates will now be equipped to diagnose and treat a multitude of conditions.
Is clinical experience necessary to become an osteopath?
Clinical experience is essential for becoming an osteopath, as it allows students to apply their theoretical knowledge in real-life situations. Most programs require extensive hands-on training.
Programs in osteopathy include, among other things, clinical placements that students are required to take while working with patients for the practical development of their diagnostic and treatment skills. Placements have been incorporated into the curriculum to ensure that graduates apply safe osteopathic principles toward independent practice within a clinical setting. The subtlety of patient care and treatment through osteopathy simply cannot be understood without this kind of hands-on experience.
What is the licensing process for osteopaths?
The licensing process for osteopaths involves passing a licensing exam after completing a degree in osteopathy. Requirements vary by country, but most regions require registration with a professional board.
Specific examinations and registration requirements differ between countries or states for individuals who wish to practice osteopathy. In addition, many countries require registering with a specific regulatory body, as is the case in the UK for the General Osteopathic Council, or in the US for the American Osteopathic Association.
In some areas, there are continuing education requirements for maintaining licensure, ensuring the practitioner is aware of the most up-to-date available techniques and knowledge.
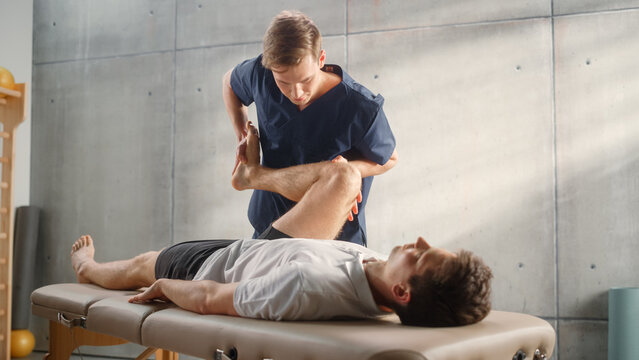
Are there any specializations within osteopathy?
Osteopaths can specialize in areas such as sports injuries, pediatric care, or cranial osteopathy. Specializations require additional training or certification beyond the standard degree.
These specializations typically involve further education and qualification; osteopaths may specialize their practice to focus on specific conditions or populations of patients. In addition to taking the practitioner’s focus deeper, specialization can also expand a practitioner’s career options by making available to them advanced treatments that can be provided in that specific field.
Specializations typically also require further learning; these updates facilitate an osteopath to keep up the specific skills demanded by the osteopathic technique.
How can you start your own osteopathic practice?
Starting an osteopathic practice requires obtaining a license, securing a location, and building a patient base. Marketing, networking, and continuous professional development are also key to success.
Building a patient base is commonly communicated through electronic media, networking, and other healthcare professionals, as well as an active community presence. There is also a majority of osteopaths who have continuous professional development and ensure that they are concentrating on the best treatment modalities to remain in competition.
Practitioners should possess balanced skills of patient care because running the practice requires clinical expertise as well as business acumen.
In Conclusion
A practitioner of osteopathy needs to undergo a confluence of academic studies, clinical exposures, and professional licensure. Perfectly trained and dedicated osteopaths can start on the journey to a very rewarding profession for health betterment in people. Once one knows how the process works, one can take the first steps toward empowerment as an osteopathic practitioner.

