- h2What is Biofeedback?
- h2What is Neurofeedback?
- h2How does neurofeedback work in the brain?
- h2What are the common uses of biofeedback?
- h2How Successful Can Neurofeedback Therapy Be?
- h2What Disorders Does Neurofeedback Treat?
- h2Is neurofeedback scientifically proven to be effective?
- h2In Conclusion

Biofeedback undeniably is a powerful self-regulation and wellness tool when considered alongside modern health interventions. They target personal health improvement but do so at different physiological levels and for various therapeutic reasons. This blog will explore what they are made of, where they can be used, and how each contributes to the management of health.
What is Biofeedback?
Biofeedback is a training technique that educates the human mind to self-regulate specific physiological processes such as heart rate, muscle tension, and blood pressure based on real-time feedback, thereby increasing health and performance through awareness and voluntary regulation.
For instance, anxiety responds better to biofeedback treatment than any other therapy because, in that case, patients learn to regulate their response to stress while treatment plans involving methods that rely on muscle relaxation to reduce pain are considered for the treatment of chronic pain.
Except for them, athletes also use it so as to better performances by improving physiological manipulation of systems in play or exercise while musicians deploy the same to optimize their playing skills based on feedback received about Tempo among others.
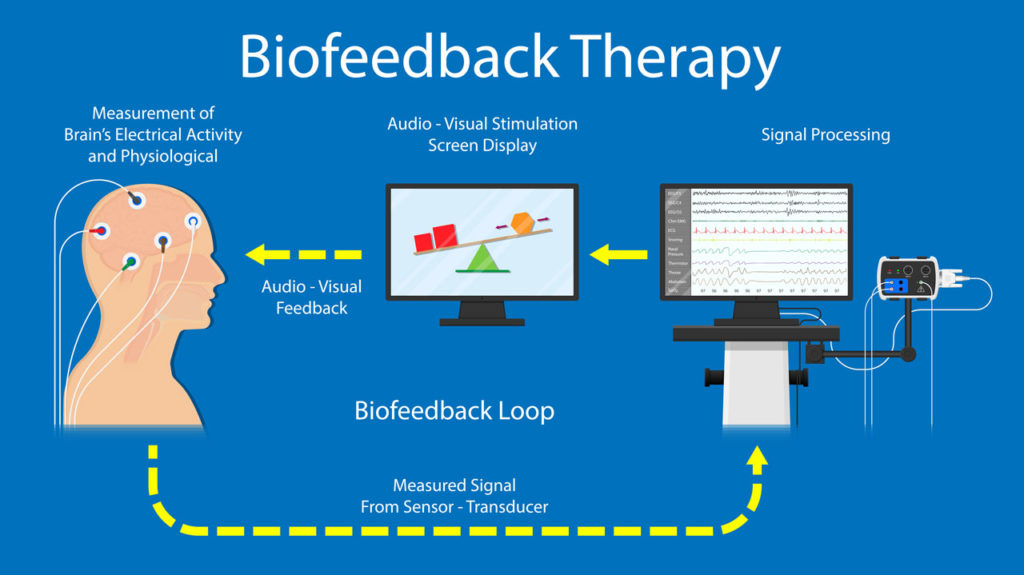
What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback is a therapeutic technique that trains the brain to self-regulate by monitoring brainwave activity. It helps improve mental health conditions such as ADHD, anxiety, and depression through real-time feedback and reinforcement of healthier brain patterns.
Neurofeedback is all about the electrical activity of the brain which is tracked and displayed through the use of EEG technology. It shows individuals how to change their brain waves in order to improve mental function and reduce neurological symptoms. ADHD can be treated with neurofeedback as it helps to increase attention while depression and anxiety are reduced through relaxation promoted by this method.
Moreover, sleep disorders are managed by altering brain wave patterns so that healthy sleep cycles may be induced. Additionally, it assists in rehabilitating cognitive functions impaired by trauma during recovery from traumatic brain injury.
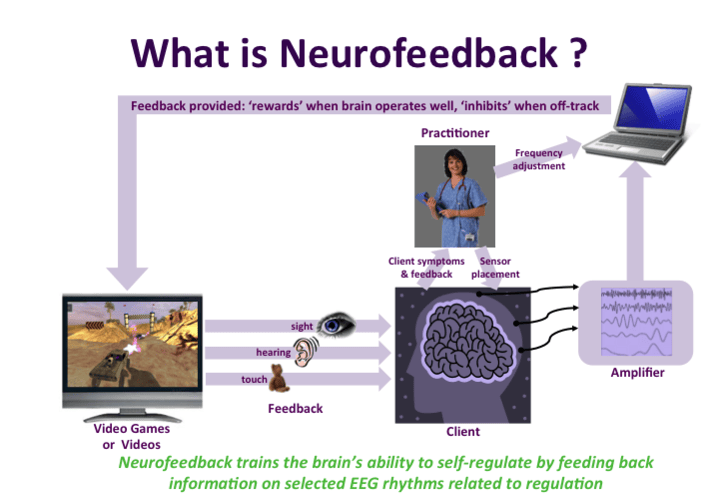
How does neurofeedback work in the brain?
Neurofeedback works in the brain by training individuals to alter brainwave activity by providing real-time feedback using EEG technology. It helps in managing conditions like ADHD, anxiety, and PTSD by promoting healthier brainwave patterns.
It improves cognitive function and brings emotional balance. During a neurofeedback session, a trained professional will walk the user through the process, allowing them to watch their brain wave activity and learn to control it so that, overtime, clear metal clarity, emotional resilience, and a better focus can be gained. It gives real-time feedback to help the participant recognize and reinforce the desirable patterns of brainwaves. This enables permanent changes in brain function and reduces symptoms of many psychological disorders.
What are the common uses of biofeedback?
Biofeedback is commonly used to treat stress, anxiety, chronic pain, and hypertension. It involves monitoring bodily functions like heart rate and muscle tension to encourage relaxation and self-regulation.
Patients learn to identify the responses to stress and modify them appropriately. This can enhance physical health and alleviate symptoms. Biofeedback allows the client to apply such techniques as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation after their physiological states have been enhanced, thus resulting in reduced stress and increased control over physical and emotional well-being.
This form of therapy makes the individual aware of the interplay between the state of their mind and physical health, thus enforcing proactive management and reduction of symptoms of stress and related conditions through regular practice and feedback.
How Successful Can Neurofeedback Therapy Be?
The success rates for neurofeedback therapy vary greatly depending on the skill of the practitioner, the level of patient participation, and the type of condition being treated. Its effectiveness is backed by research, primarily in terms of addressing behavioral symptoms related to ADHD and alleviating anxiety.
There are many accounts from patients themselves or those who have worked with them in a clinical setting that describe profound changes following treatment. This recognition has contributed significantly towards increasing its use throughout different medical communities. Nevertheless, people must have realistic expectations and know-how grounded scientifically so they don’t get misled about what can or cannot happen through this form of therapy.

What Disorders Does Neurofeedback Treat?
Neurofeedback helps treat disorders such as ADHD, anxiety, depression, PTSD, and sleep disorders. By training the brain to self-regulate, it improves mental health and cognitive function, offering a non-invasive, drug-free therapy option.
The range for applying neurofeedback is wide because it treats disorders by modifying brain activities at their foundation. Specifically, attentional control is improved during treatment for ADHD while stabilizing fluctuations in moods may help alleviate anxiety along with depression.
Sleep problems and learning disabilities are also targeted by normalizing waveforms associated with restfulness or wakefulness within various areas across our mindscape. Understanding individual brain mechanisms remains key to successful customization according to needs when engaging in such treatments.
Is neurofeedback scientifically proven to be effective?
Research supports neurofeedback’s effectiveness for conditions like ADHD, anxiety, and PTSD, showing positive outcomes in numerous studies. While results vary among individuals, many experience significant improvements in symptoms.
Neurofeedback is often utilized in conjunction with other treatments to yield the best possible results. Research into its further applications is ongoing. For example, neurofeedback is able to reduce the level of anxiety and improve attention in patients with ADHD; it has also been shown that neurofeedback enables long-term changes in brain activity, which makes it a very promising additional treatment in complex therapy schemes.
While this may vary in experience, neurofeedback does show promise in improving general well-being, and the application is on the increase as continued research validates its effectiveness in improving various neurological and psychological ailments.
In Conclusion
Biofeedback and neurofeedback help one improve their health individually by providing various ways through which they can deal with different conditions. They work best if only we understand how they work and use them appropriately whenever necessary. To achieve this people should seek advice from experienced professionals who will guide them on what steps need to be taken during treatment so that it becomes effective. Hence, this proves that indeed healthcare should always be tailored according to each person’s needs thereby making life better for all individuals within the society.
