Neurofeedback and biofeedback: Despite challenges and controversies ranging from scientific validity to ethics, increasingly used to treat many mental and physical health ailments. The purpose of this information is to help practitioners and patients make informed decisions based on a well-rounded view of the area.
What Are the Main Challenges of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback?
The Main challenges of neurofeedback and biofeedback include limited scientific evidence, high costs, and inconsistent results. Skepticism arises due to the lack of standardized protocols and varying outcomes. While some find these therapies effective, others question their long-term benefits and accessibility.
Neurofeedback and biofeedback do not have scientific evidence, which raises many questions in the medical field. High-cost barriers also give way to access that is only limited to a few stringent ones due to lack of insurance coverage. Varied protocols also lead to mixed results thus causing controversy over their effectiveness or otherwise.
It seems revolutionary to some while others believe it has not provided enough evidence for long-term therapy. Good training of the practitioners and education among the patients are sine qua non in that regard to overcome such barriers.
Why Is Neurofeedback Considered Controversial?
Neurofeedback is considered controversial due to inconsistent evidence, varied training methods, and high costs. Critics argue that its efficacy lacks consistent scientific support. While some patients experience benefits, the controversy revolves around its reliability and accessibility.
The controversy about neurofeedback stems from a lack of standardized scientific evidence and heterogeneity in training protocols. The heterogeneity of approaches among practitioners raises questions about the reliability of the treatment.
The rising controversy surrounding neurofeedback arises from the fact that the sessions have such high costs that most cannot afford them. Therefore, without a reasonable scientific basis and regulation, some critics say that the actual benefits of neurofeedback cannot be even established through positive anecdotal experience.
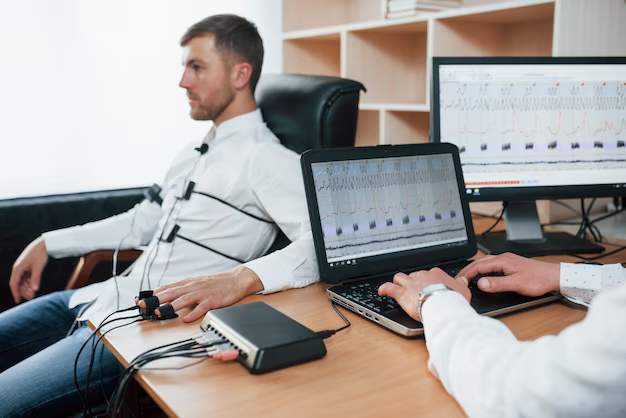

What Ethical Concerns Are Associated with Biofeedback?
The ethical concerns associated with biofeedback include patient safety, data privacy, and informed consent. Ensuring accurate data interpretation and secure handling of patient information is crucial. Ethical dilemmas arise when practitioners promise more than the technique can deliver.
Biofeedback ethics issues involve protecting the privacy and safety of patients and handling information. There should be correct analysis in order not to mislead patients with the results obtained. Patients have to be first informed on what treatment it is and what shortfalls to expect.
Then, some practitioners may sometimes unknowingly promise more than they can deliver, thus putting them into ethical dilemmas between giving patients expectations and what eventually materializes. Responsible practices and establishing trust with the patients work through the settlement of these ethical issues.
Is Neurofeedback Scientifically Proven to Be Effective?
Neurofeedback is proven to be effective with limited scientific consensus. Some studies show positive outcomes for conditions like ADHD and anxiety, but others question its long-term efficacy. The variability in results fuels ongoing debates.
The scientific proof of neurofeedback’s effectiveness varies. Some research indicates positive outcomes for conditions such as ADHD, anxiety, and depression. However, the lack of large-scale, double-blind studies makes it challenging to draw definitive conclusions.
Critics argue that placebo effects or individual variability may account for reported benefits. As a result, while neurofeedback shows promise, its scientific standing remains a topic of debate, needing more robust and consistent research.
Why Is the Cost of Biofeedback a Challenge?
The cost of biofeedback is a challenge due to expensive equipment and training. High session fees make it less accessible. Limited insurance coverage adds to the financial burden for patients seeking long-term treatment.
Biofeedback therapy involves costly equipment and requires specialized training for practitioners, leading to high session fees. These expenses can accumulate, making it difficult for many individuals to afford prolonged treatment.
Additionally, biofeedback is often not covered by insurance, leaving patients to pay out-of-pocket. This financial barrier limits access to those who could benefit, posing a significant challenge in the broader adoption and accessibility of biofeedback therapy.
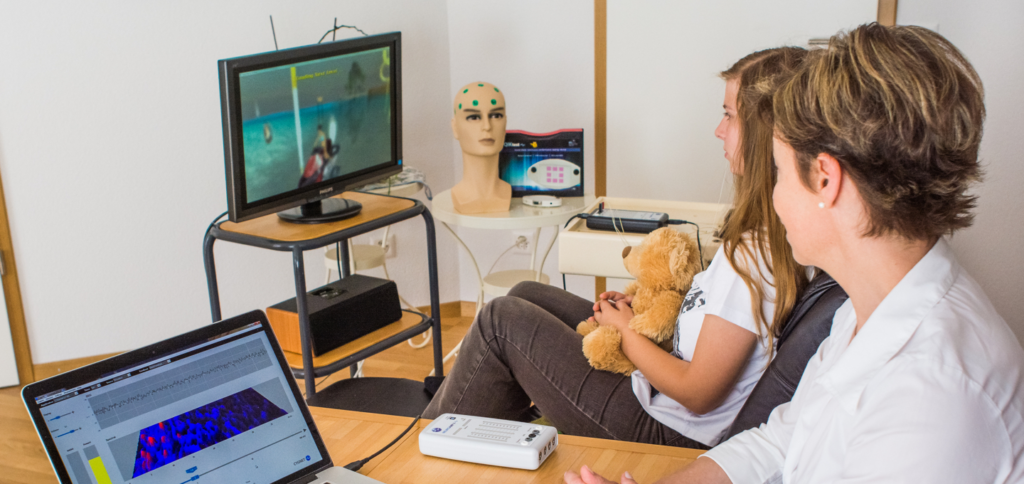

How Can Inconsistent Results Affect Neurofeedback's Reputation?
Inconsistent results affect neurofeedback’s reputation by raising doubts about its reliability. Patients’ experiences vary, leading to mixed reviews. These variations contribute to skepticism within the medical community and among potential patients.
Neurofeedback’s inconsistent results affect its reputation by creating uncertainty about its effectiveness. While some patients report significant improvements, others see little to no change, leading to mixed opinions.
This inconsistency makes it difficult for healthcare professionals to confidently recommend neurofeedback. The varied outcomes contribute to skepticism within the medical community and among potential patients, who may be hesitant to invest time and money in a therapy with unpredictable results.
What Are the Risks of Using Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Without Proper Training?
The risks of using neurofeedback and biofeedback without proper training can lead to misinterpretation of data and incorrect treatments. Risks include ineffective therapy, patient harm, and ethical violations. Proper training ensures safe and effective practice.
Poor training in neurofeedback as well as biofeedback can result in misinterpretation of data and further inappropriate plans of treatments. Therapy may not be effectively carried out, and in some instances, the patient may worsen or get worse.
In addition, the practitioners with lack of extensive training might unknowingly violate the ethical standards-not only to, for instance, obtain patient consent and safety but also to conduct these therapies appropriately. Therefore, proper training and certification are rather important for safely and effectively performing these therapies.
In Conclusion
Neurofeedback and biofeedback have both benefits and problems. Some of these problems include limited scientific evidences, high costs, ethical concerns, or inconsistent results. It is best that the patients and the practitioners are well-informed of these complexities in their approach to treatment. Addressing neurofeedback and biofeedback problems properly with proper training, ethical practice, and further research may be able to unveil these strategies and integrate them into holistic healthcare approaches.
