
Homeopathy is an alternative medicine which was established in the 18th century. It has become a matter of debate in recent times. Despite this, patients still find solace in it while scientists are concerned about its effectiveness and basic theories.
What Are The Basic Principles of Homeopathy?
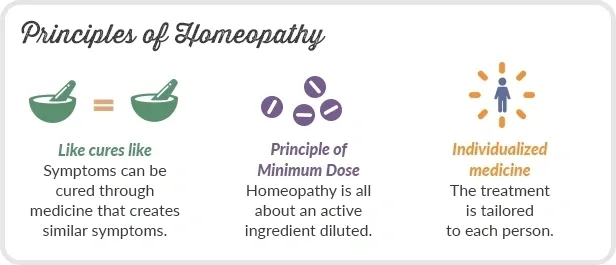
The basic principles of homeopathy include “like cures like,” using highly diluted remedies, individualizing treatment, and stimulating the body’s natural healing processes.
To understand why it attracts such criticisms, one has to have an understanding of homeopathy itself.
Law of Similars in homeopathic medicine is that anything that can create reactions and symptoms in healthy humans can be used to treat those affected by diseases.
Water or alcohol is used to dilute homeopathic remedies until there is no remaining trace amount of the original substance. In general, homeopaths administer their treatments based on overall symptoms rather than targeting particular diseases or conditions.
What Are The Scientific Criticisms of Homeopathy?
Scientific criticisms of homeopathy include lack of empirical evidence, reliance on placebo effects, implausibility of dilution principles, and inconsistent results in clinical studies.
One notable challenge to homeopathy comes from the fact that it operates against all known scientific principles. It’s often true that most dilutions used for homeopathic remedies do not have any detectable quantity of medicinal particles inside them. Critics claim these preparations can only exist as placebos since they lack enough molecules.
In pharmacology, it is commonly held that drug effect is related to its dose. According to homeopathic principles higher dilutions result in stronger potencies (‘similia similibus curantur’). Most medical experts believe that the homeopathic principles go against science.
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of clinical trials have repeatedly failed to establish the effectiveness of homeopathic medicines over placebo for any medical condition.
What Are The Ethical and Practical Concerns?
Ethical and practical concerns in homeopathy include misleading efficacy claims, potential delays in conventional treatment, lack of regulation, and reliance on placebo effects over evidence-based care.
Experts argue that a lack of trust in conventional medicine may induce patients to delay appropriate treatment, which may aggravate their condition further. The issue becomes more pertinent with severe or life-threatening diseases where early treatment can make all the difference.
In certain countries, such treatments are part of national health services or covered by private insurance plans. This diverts limited healthcare resources away from evidence-based treatments and towards possibly less effective alternatives.
Some people see advocacy for homeopathy as a factor contributing to scientific illiteracy among individuals. By upholding principles that go against basic scientific beliefs, homeopathy may undermine confidence in evidence-based medicine as well as science itself.
What Are The Regulatory Issues In Homeopathy?
Regulatory issues in homeopathy include inconsistent standards, lack of rigorous efficacy testing, varying legal status globally, and concerns about consumer protection and misleading claims.
Most of these homeopathic products are often advertised using grounds that lack scientific evidence.
Different companies might produce homeopathic preparations differently. Critics posit that poor standardization makes it hard to ensure consistency in the quality and safety of these products.
Supporters of homeopathy commonly cite positive experiences by patients as proof of its effectiveness. However, skeptics attribute this to the placebo effect, the natural power of healing, together with empathetic care, which is usually offered by homeopathic practitioners.
While acknowledging that the placebo impact is a genuine phenomenon that may be beneficial, critics contend that prescribing placebos without disclosing such information to patients is unethical.
What defines homeopathic?
Homeopathy is defined as the use of highly diluted substances to treat symptoms based on the principle of “like cures like,” aiming to stimulate natural healing.
Homeopathy, an alternative medical system, is a system that follows the concept of “similia similibus curentur” whereby substances that cause symptoms in healthy people are used in extremely diluted form to treat similar symptoms in sick people. It also involves use of minute quantities of highly diluted substances which are said to spur the body into self-healing process.
Is homeopathy good or bad for you?
Homeopathy’s effectiveness is debated; some find it helpful, but scientific support is limited. It can be safe if used responsibly, complementing conventional care.
The efficacy of homeopathy is debated. Some users report positive results, often attributed to the placebo effect. Nonetheless, scientific studies have generally found no significant benefits beyond placebo. When used along with other treatments it is considered safe but relying only on it for serious conditions can be dangerous.
Is Homeo banned in Germany?
Homeopathy is not banned in Germany; it remains legal and widely practiced, though its effectiveness and coverage by public health insurance are increasingly debated.
Germany did not ban the practice of homeopathy. Instead, it has a great tradition related to this form and thus, it gets formal recognition and regulation. A few health insurance plans even cover some German pharmacies who stock different homeopathic remedies. Nevertheless, its effectiveness still remains under evaluation and criticism.
What is the most controversial part of the homeopathic method?
The most controversial part of the homeopathic method is the use of highly diluted substances, which critics argue lack scientific evidence and rely on placebo effects.
This dilution stage renders homeopathic remedies a subject of extreme controversy as it usually goes so far that there is no original substance’s molecule remaining inside their composition at all.
Detractors argue that this contradicts basic tenets of chemistry and pharmacology known in science thereby making it questionable how such dilutions could have any therapeutic impact apart from the placebo effect.
What does 30C mean in homeopathy?
In homeopathy, 30C means the substance has been diluted 1 part in 100, repeated 30 times, resulting in an extremely diluted remedy.
In homeopathy, 30C refers to dilution where the mother tincture has been diluted by one part a hundred thirty times. In this case, it implies that one part of the substance would be diluted in 10^60 parts of water or alcohol. This practice is controversial and typically involves extreme dilutions.
Do doctors believe in homeopathy?
Belief in homeopathy varies among doctors; some are skeptical due to lack of scientific evidence, while others may support its use for certain conditions or patient preferences.
Doctors have differing beliefs when it comes to homeopathy. In some regions where it’s more culturally acceptable, some medical practitioners incorporate them into their procedures. However, the majority of mainstream medicine and health organizations regard it with skepticism since there is no proven scientific evidence.
Conclusion
The main criticisms against homeopathy are its lack of scientific plausibility, limited evidence for efficacy, placebo effects, and concerns about public health. Even though some patients might claim they are benefiting from such treatments, science overall remains suspicious about such assertions. As healthcare systems and consumers continue to debate on this matter, they should carefully weigh all evidence surrounding these practices.
