Neurofeedback and Biofeedback: The Power of the Mind-Body Connection
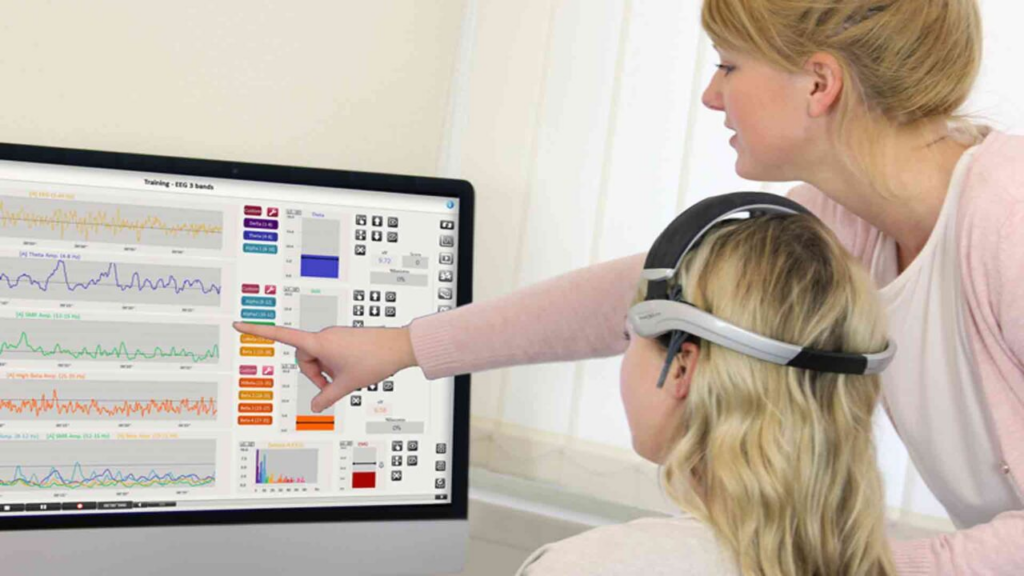
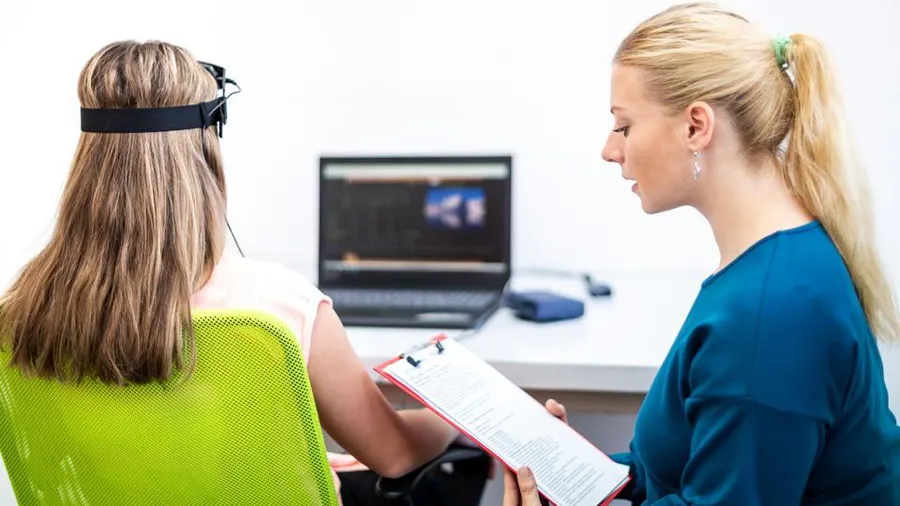
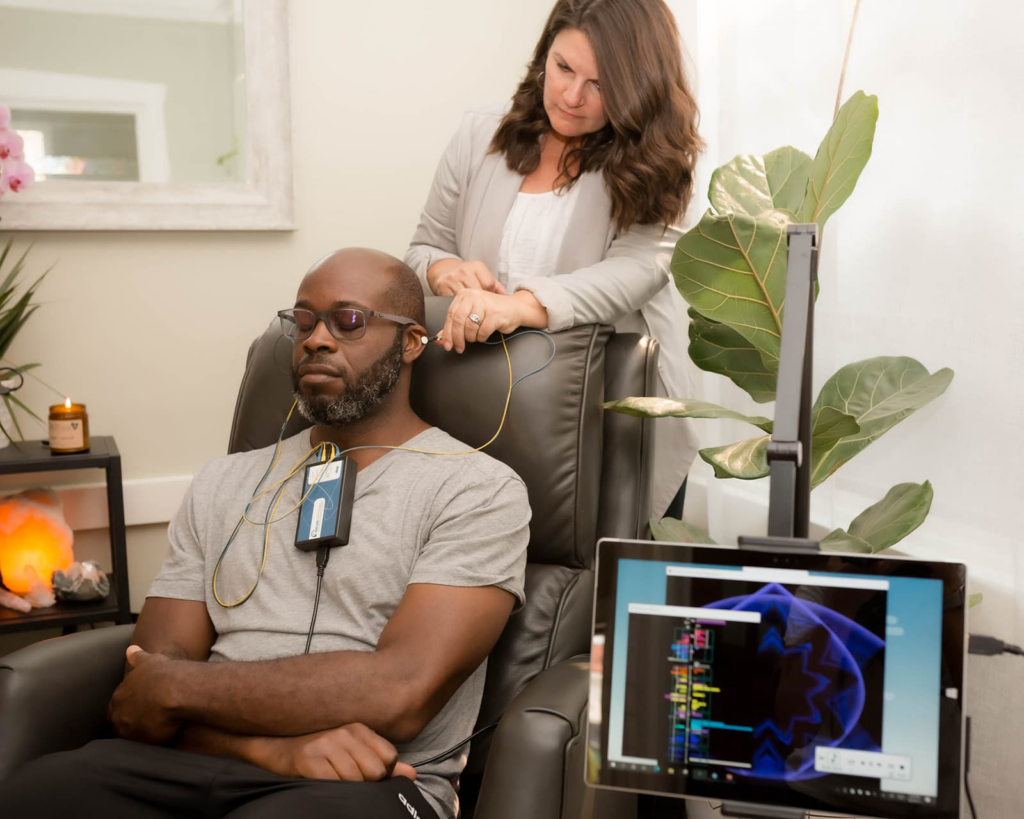
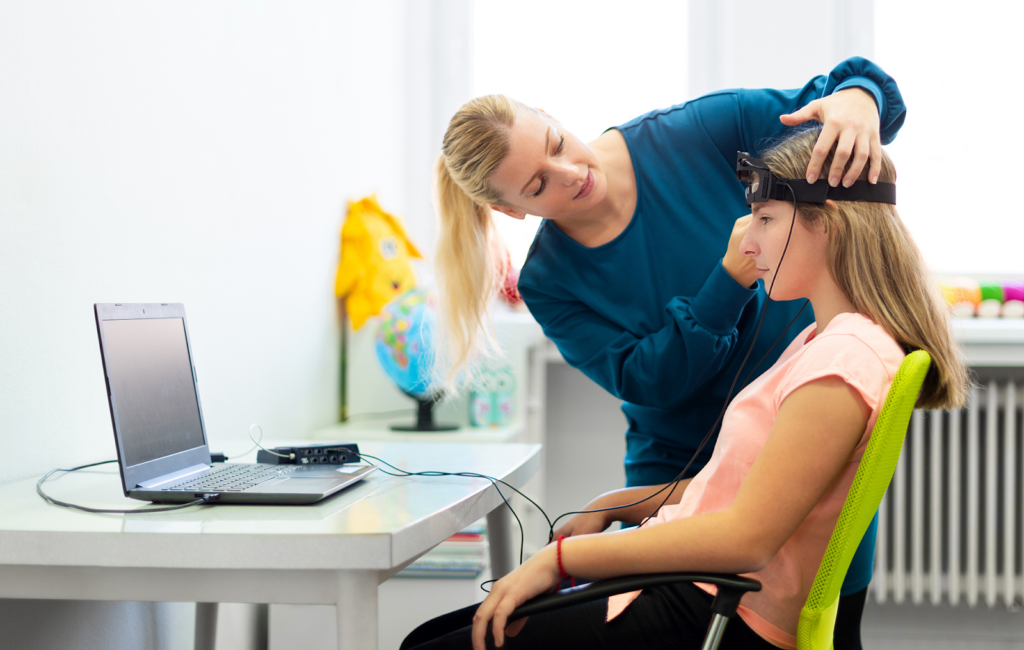
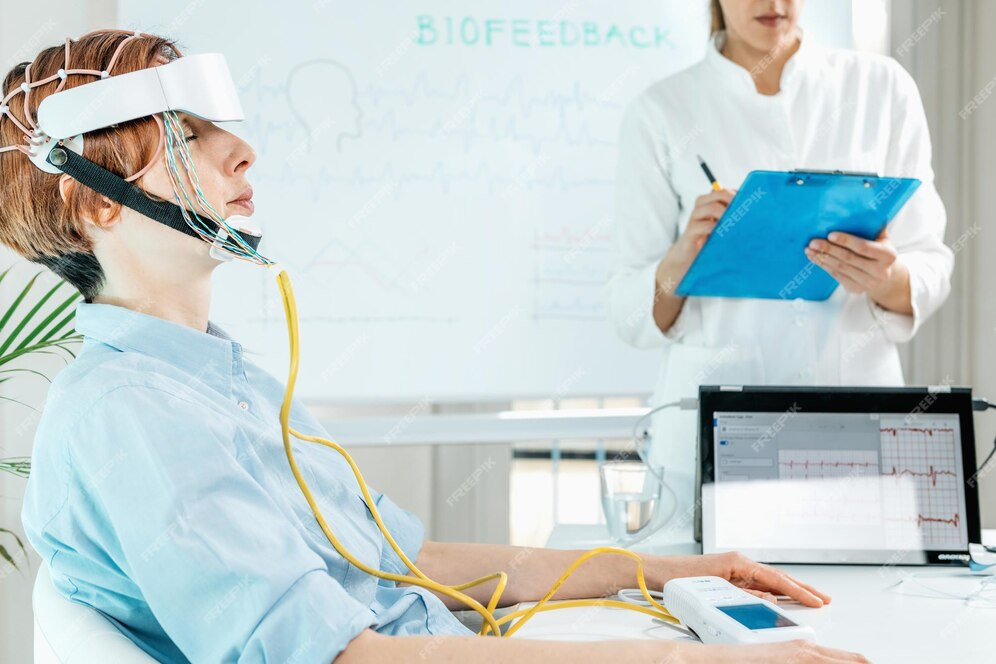
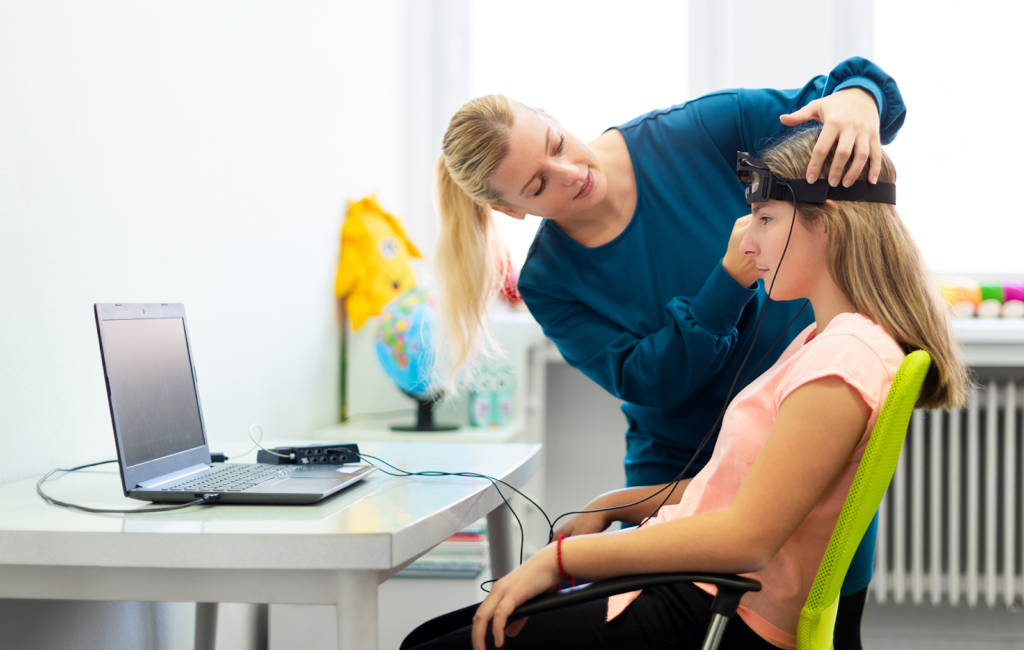
Over the past few years, there has been a noticeable rise in the use of non-invasive techniques. The two such methods which have attracted considerable research interest are neurofeedback and biofeedback. They also offer new dimensions in improving health and wellness by enabling a person to actively control their body and brain activities. Having a Full Understanding of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback In neurofeedback and biofeedback therapy, any physiological activity of the patient is observed and is employed for healing oneself. Thus biofeedback encompasses feedback from the “biology”, but at the same time addresses other ‘biological’ inputs of the body, thus incorporating the use of electroencephalograms as a part of the biofeedback therapy. Helping an individual to cope with and dismantle his/her condition or suppressing a person’s symptoms, in most cases physical relaxation techniques or medication the essence of behavior. Biofeedback therapy also called ‘feedback therapy’ where patients are equipped with biomedical sensors measuring heart rate, temperature, and muscle tension. Among many others, after the assessment, physiological processes are altered through the exercise of relaxing or engaging the mind. There is currently no surgery put in place to enhance both mental and physical well-being since they propel the degrees of consciousness and let control over bodily actions. Both approaches make use of and integrate the brain plasticity track and operant conditioning into pure science since both methods are dependent on this. In particular, they have been used in tackling a number of health issues. Fundamental Concepts and Techniques of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Technically, neurofeedback and biofeedback are the types of techniques that help a person to self-regulate by training to control physiological processes. Neurofeedback deals with brain wave activities leading to conscious modification of actual brainwave patterns by using feedback derived from real-time EEG. Neurofeedback is strongly used in curing cases like ADHD, anxiety, and sleep disorders by providing more balanced brainwave states. Biofeedback extends to physiological functions, like heart rate, muscle tension, skin temperature, and breathing, through sensors to give feedback about the processes so that people can learn to control them voluntarily. Some of the most common techniques used are HRV training for heart rate and EMG biofeedback for muscle relaxation. Actually, both such methods draw on the operating conditioning model, by which people learn in the present by tuning into their body’s responses and knowing how to revise them. As training progresses, it will probably be that an improved regulation of one’s self translates into health benefits and then results in enhanced mental and physical performance. Process and Equipment in Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Technique Process Steps Equipment Needed Home Practice Neurofeedback Assessment, Sensor Placement, Feedback Presentation, Training, Progress Monitoring EEG sensors, visual/auditory feedback systems Limited by the need for equipment Biofeedback Initial Assessment, Sensor Placement, Feedback Presentation, Training, Home Practice HRV monitors, EMG sensors, thermal sensors, respiratory sensors, GSR sensors More feasible with portable devices and apps This table provides a structured view of the process and equipment involved in neurofeedback and biofeedback. Exploring the Healing Benefits of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback These are non-invasive therapeutic techniques that bring such big benefits from physical to the health of the mind. It helps individuals manage the physiological process, which allows them to have control over self-regulation, mental well-being, and overall health. Based on real-time monitoring of brainwaves, heart rate, and other body functions, people can control their response to stress, anxiety, and other challenges. Here is an overview of their healing benefits: Enhances Self-Regulation: Both neurofeedback and biofeedback teach individuals to control brain activity and physiological processes, improving emotional responses, mental clarity, and overall physical well-being. Treats Various Mental Health Conditions: Neurofeedback is effective in managing ADHD by improving focus and reducing hyperactivity, while also helping with anxiety, depression, PTSD, and sleep disorders through brainwave retraining. Alleviates Chronic Pain: Biofeedback helps reduce muscle tension and manage pain for conditions like migraines and fibromyalgia by increasing body awareness and promoting relaxation. Improves Cardiovascular Health: Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback strengthens heart health, aiding in the regulation of heart rate and breathing, and helps manage hypertension. Scientifically Backed: Neurofeedback uses brain plasticity to retrain brainwave patterns, while biofeedback leverages operant conditioning, both supported by research for effective stress reduction and health management. The holistic benefits are resultant benefits that develop the perception of better awareness and control over body responses in the management of their mental and physical health conditions Process of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback The stage called evaluation is the first one which is adduced prior to the introduction of either the neurofeedback or biofeedback process – a therapist looks for brain waves from a patient or any other physiological parameters using gadgets such as headgear used for neurofeedback or sensors to detect muscle and skin temperature, heart rate for biofeedback equipment. This data decides on which feedback and how much of it should be engaged during the course of the training. This process is classified under one type of feedback which is called neurofeedback whereby the learner is able to view explanatory pictures depicting their brain waves and learns to use mental effort duly available to manipulate it to make particular inputs such as a relaxing the alpha or beta wave or focusing. It encompasses the utilization of a few forms of feedback for instance relaxation training, which aims to regulate certain physical activities or functions like heartbeats and muscular tension, to which are integrated trainable breathing techniques. The Science and Research Behind Neurofeedback and Biofeedback Neurofeedback Research It has been found that this form of therapy helps with ADHD, anxiety disorders, and sleep disorders. Some studies have reported significant effects of neuro-feedback on hyperactivity/impulsivity among those suffering from ADHD. It should be noted, however, that researchers have called for more robust controlled research to verify its effectiveness. BioFeedback Research A lot of research supports the use of biofeedback for different conditions. Some studies found strong support for the efficacy of biofeedback as a treatment modality for headaches, anxiety, and hypertension. Common Myths and Misunderstandings of Neurofeedback and Biofeedback