Discover Your Perfect Healer Today!
Our online practitioner directory connects you with a wide range of healers to suit your unique needs.
Easily search and find the right professional to support your wellness journey.
Start exploring today to find your perfect match.
Modality
Disease
Books
Products
Events
Training
Blogs
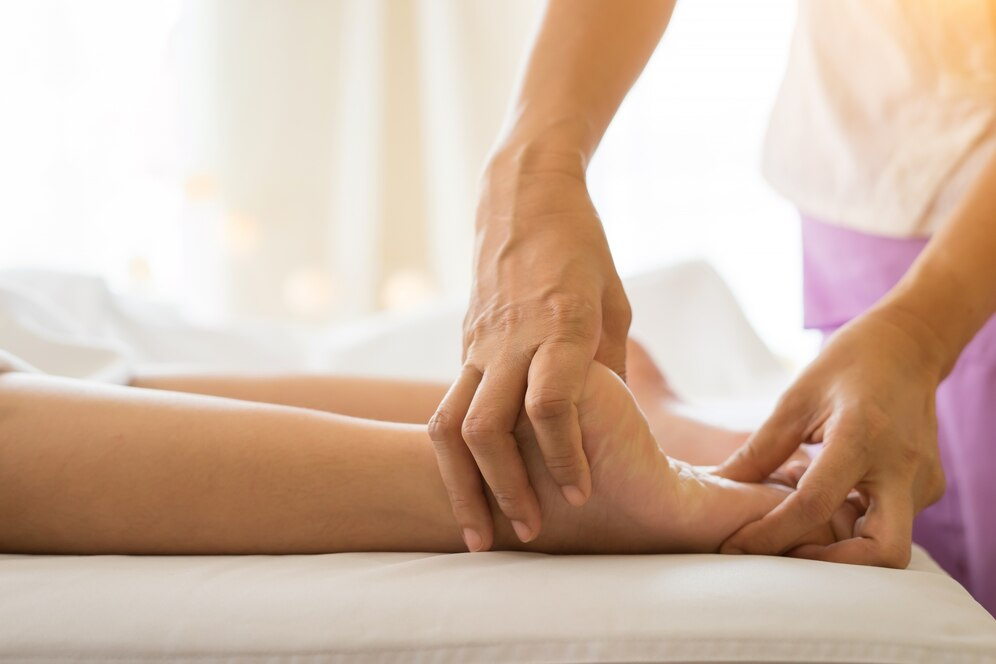
Reflexology
Healing Benefits of Reflexology: An In-Depth Exploration
Reflexology is an all-inclusive therapy that aims to be applied at certain points on the feet, hands, or ears, exerting pressure through these applications. This ...
Read More → Written by
John Smith
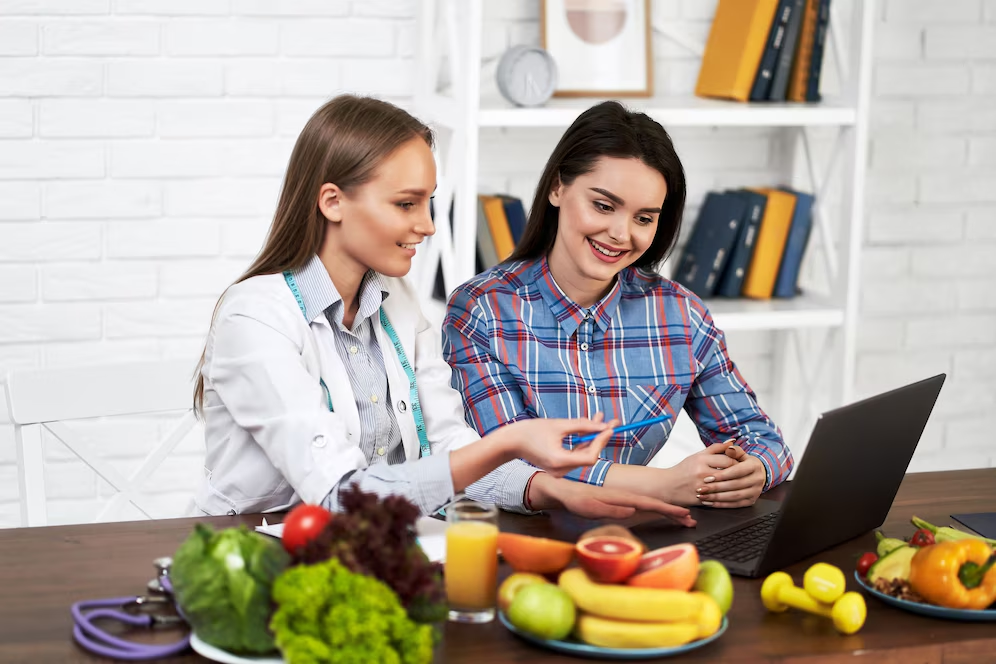
Nutritionist
Unlock the Benefits of Nutritionist: A Comprehensive Guide
Nutritionists are integral to better health. They provide individually tailored dietary advice and guidance. It could make a big difference to consult a nutritionist, whether ...
Read More → Written by
John Smith
Physical Therapy
The History of Physical Therapy: Evolution and Milestones
The history of physical therapy is as old as several thousand years, stemming from ancient methods of healing to a modern medical discipline. It has ...
Read More → Written by
David Brown
Homeopathy
Key Concepts and Techniques in Homeopathy Explained
Homeopathy is a system of medicine that is different from orthodox medicine in its ideology and treatment methods as it takes care of the individual. ...
Read More → Written by
James Williams
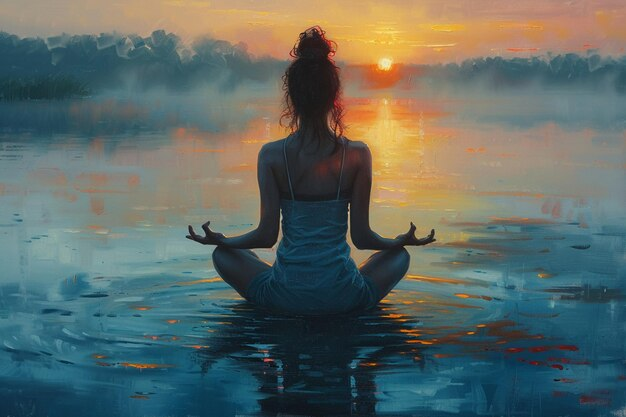
Meditation
Expert Tips for Maximizing the Healing Potential of Meditation
All healing benefits- mental clarity, emotional balance, and even physical well-being-of meditation can be achieved. But it takes more than just setting up the basics ...
Read More → Written by
John Smith
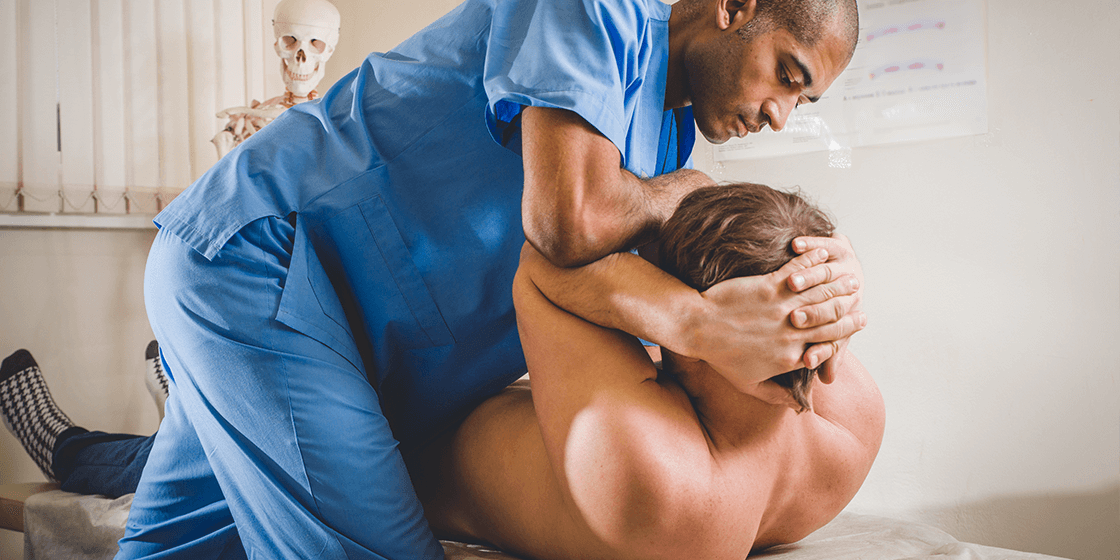
Chiropractor
What to Expect During a Chiropractic Session: A Step-by-Step Guide
Conveniently combined with several approaches is a chiropractic procedure which mainly aims at achieving spinal health and general well being and as a result everyone ...
Read More → Written by
James Williams