The Role of Borrelia Burgdorferi Bacteria in Lyme Disease
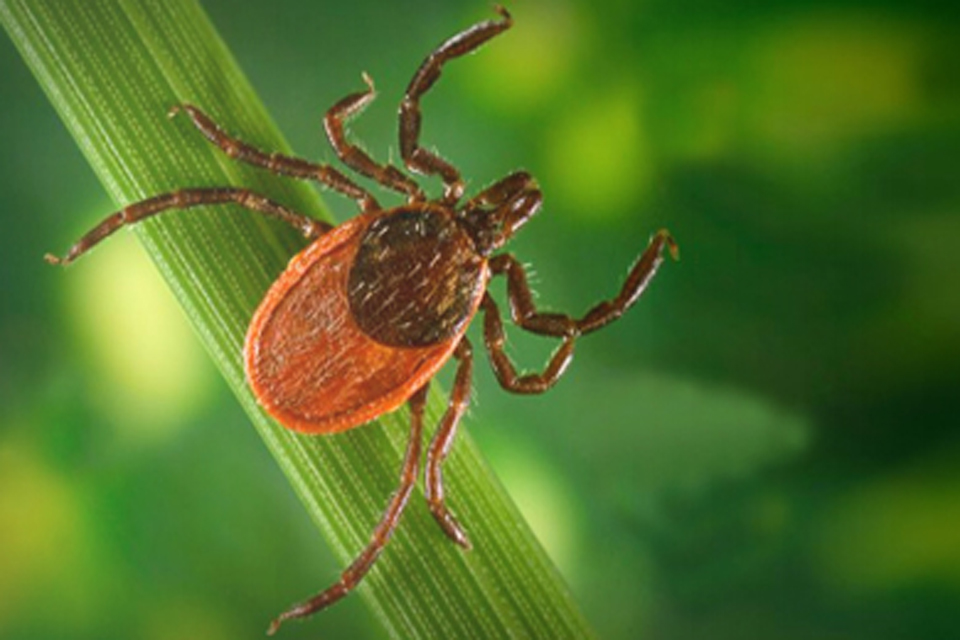


Understanding Lyme disease and how this bacterium infects humans is vital for preventing and managing Lyme disease. By knowing more about the role of Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria in Lyme disease, individuals can be careful about tick bites and reduce their risk of infection.
What is the role of Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease?
The role of Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease is to multiply itself in the human body when transmitted through tick bites and cause infections. When the tick feeds an infected animal, it becomes infected and the bacteria grows in a tick’s gut, transforming to its saliva. When the tick bites a human it’s saliva enters the bloodstream, creating the signs of infection, known as Lyme disease.
Borrelia burgdorferi enters into tissues and joints, causing various symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue. A bull’s eye rash developed in the area of the tick bite. It is considered a primary symptom as other symptoms can overlap other conditions. When it is unnoticed or not treated, the bacteria can then multiply itself in the bloodstream and affect various organ systems. This can result in long-term health complications like joint pain or even neurological complications.
How does Borrelia burgdorferi cause infection in humans?
Borrelia burgdorferi causes infection in humans by entering the bloodstream through tick saliva during feeding. The bacteria multiplies itself through tissues and begins spreading throughout the body.
Early symptoms include fever, chills, fatigue, and a bull’s-eye rash (primary symptom). If not treated, the bacteria can spread deeper into tissues, leading to inflammation of the joints, affect various organs like heart complications, and neurological issues, including facial paralysis.
Early treatment involves antibiotics is very effective for the infection at the early stage. The sooner you understand the early signs and get medical help, it can be helpful to prevent the bacteria cause long-term problems of Lyme disease.

How do ticks carry Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria?
After feeding on infected animals, like rodents or deer, ticks carry Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria. After the bacteria enter the tick, they multiply in its gut. Over time, the bacteria gets into the tick’s salivary glands.
When the tick attaches to a human skin and feeds, it injects saliva containing the bacteria into the host’s skin and bloodstream. Ticks are the primary vector through which Lyme disease is transmitted. The spread of Borrelia burgdorferi can be stopped, inspecting for regular tick checks and avoiding bites.
Knowing about how ticks acquire and carry the bacteria helps the need for controlling tick populations to reduce the risk of Lyme disease.
What are the symptoms caused by Borrelia burgdorferi?
The symptoms caused by Borrelia burgdorferi include fever, chills, joint pain, malaise, arthralgias, and an Erythema Migrans (EM). When the treatment for infection is delayed it leads to more serious issues like arthritis, neurological complications, and heart problems at more advanced stages of Lyme disease.
The bacteria can cause serious joint pain and swelling in knees and even neurological issues such as facial paralysis and memory loss if it persists in your body for a long time. It causes irregular heartbeats or inflammation of the heart tissue.
Early symptoms should be observed and seek medical care immediately with antibiotic treatment for Lyme disease. It prevents the development of chronic health complications.
How can Lyme disease from Borrelia burgdorferi be prevented?
Lyme disease from Borrelia burgdorferi can be prevented by wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, and performing regular tick checks after outdoor activities. Promptly removing attached ticks reduces the chance of Borrelia burgdorferi transmission. Avoiding high-risk tick habitats is also recommended.
Use tick repellents that contain DEET or permethrin. After spending time outdoors, conduct thorough tick checks on your body, paying attention to areas like the scalp, armpits, and behind the knees.
If you see a tick, immediately pull it out with tweezers. Early removal minimizes the transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi. High-risk habitats, like tall grasses, and vigilance about ticks are key in avoiding Lyme disease.
Can Borrelia burgdorferi cause chronic Lyme disease?
Borrelia burgdorferi can lead to chronic Lyme disease if left untreated. It causes symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, and memory problems. The condition is also commonly referred to as chronic Lyme disease or post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS). It involves persistent fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain even after initial treatment and even if there is no infection persists.
Some individuals may suffer from cognitive impairments, including the inability to remember or focus. The pathogenesis of PTLDS has not yet been determined, but early treatment with antibiotics helps prevent all chronic complications after Lyme disease. Symptoms must be recognized immediately and appropriate medical treatment sought. All these can prevent chronic complications of Lyme disease.
Why is Borrelia burgdorferi important in tick-borne disease research?
Borrelia burgdorferi is a bacteria important in tick-borne disease research. It causes Lyme disease, which is the most common tick-borne illness. Its biology can be studied to further improve the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease and to enhance the overall understanding of tick-borne diseases.
By understanding the bacteria’s unique characteristics such as the immunity evasion characteristic, scientists could develop new antibiotics and test whether a vaccine is possible.
In addition, the study on Borrelia burgdorferi highlights diseases that are transmitted by ticks: control and mitigation of other tick-borne infections. It ensures better public health measures at the same time that result in reduced impact from worldwide tick-borne diseases.
Wrapping Up!
Understanding the role of Borrelia burgdorferi in Lyme disease is critical in its prevention and treatment. Knowledge of how this bacterium spreads and how it creates symptoms will allow an individual to take necessary measures for protection against tick bites. Detection at an early stage, followed by proper treatment, helps avoid severe complications and properly manage this common tick-borne illness.
